4.5.14. Pay for Results: Advance Market Commitments
DESCRIPTION
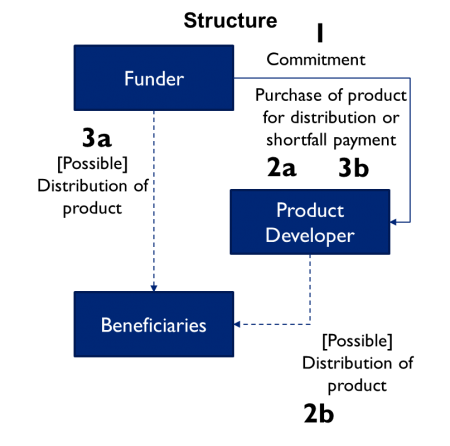
Agreements to guarantee a price or market for a product upon its successful development, as a way to mitigate uncertainty in building products/markets (initially used to encourage vaccine production).
CONSTRAINTS ADDRESSED
- Appropriate capital to meet borrower needs
- Production costs associated with target sector/region
- Rate of return on lending in target sector/region
ADVANTAGES
Creates market incentive for private sector research and development (R&D), Downside production risks for Finance Seekers, Unfavorable Enabling Conditions for Finance Seekers
DISADVANTAGES
From the perspective of designers:
- Setting the price too high creates the potential for a windfall benefit for the manufacturer/service provider at the expense of the funder(s). Setting the price too low may not sufficiently mitigate the risk in product development and marketing, and the product may therefore not be developed
- Avoiding a “winner take all” situation and creating a true market for products that can be commercially available and marketed in developing countries
- Payment upon full development of a product inadvertently discourages smaller firms from participating, as upfront investment costs are extremely high
Image
From the perspective of manufacturers/service providers:
- Funding is only provided when new products are fully developed
- Ensuring AMCs are legally binding and enforceable in courts
- Ensuring copy-cat products will not take up the guaranteed market
From the perspective of developing countries:
- Contributing to some of the development costs
- Ensuring long-term affordable prices on developed products
MUST HAVE’S, CRITICAL POINTS, OR QUESTIONS TO CONSIDER
AMCs are most appropriate when a solution to the development challenge is clear, but commercial viability is not because demand is uncertain; manufacturers exist and can be encouraged to bear the cost of developing products; sufficient donors exist to share financial risk; potential market size is significant enough to stimulate more R&D.
VIGNETTE: USAID/UNICEF ZIKA ADVANCE PURCHASE COMMITMENT (GLOBAL)
SITUATION
Developing a Zika virus point-of-care diagnostic test is complicated by the short time the virus stays in the body. UNICEF and USAID are using an Advance Purchase Commitment (APC) to decrease manufacture risk in diagnostic development.
STRUCTURE
This is USAID’s first APC to accelerate development and scale-up of rapid in vitro ZIKV diagnostics. USAID will provide $10M to guarantee the purchase of diagnostics over three years.
IMPACT
In April 2019, UNICEF and USAID announced the three firms who have been contracted as product developers until late 2020.

